As we know, climate change is a real societal problem and governments are gradually taking action. Thinking about these measures, I have paid attention to vehicles. More and more users are being urged to buy 100% electric cars, but what about commercial vehicles? These vehicles make thousands of journeys every day and we do not see an increase in the use of electric cars in industrial sectors.
From here, I have become curious and I have researched a little about the alternatives on the market and whether some companies are already putting these vehicles into practice or testing them.
VOLVO FE and FL Electric
These two models have been the first two launched by the Swedish brand. The difference between both is the load capacity, being the FE the one destined to the heaviest operations. They will be able to support a gross weight between 15 and 27 tons depending on the model
The first Volvo FE Electric, in a garbage collection version with a superstructure developed together with Europe’s largest bodybuilder, Faun, started operating in early 2019 in Germany’s second largest city, Hamburg..
Composed by two electric motors that offer a maximum power of 370 Kw. They have a range between 200 and 300 km. They take an hour and a half to charge.
Mercedes Eactros
The Mercedes proposal is called Eactros and is a truck with a range of 200 km and a maximum gross weight of 18 and 25 tons depending on the model.
Man TGM 26.30E
Is a vehicle with an electric motor located in the centre of the frame, generating 264 kW maximum load is 26 Tn. The truck offers a range of 180. According to the manufacturer, this vehicle, designed for use in urban logistics.
Mitsubishi Fuso Ecanter
Fuso is the commercial variant of the Mitsubishi brand and the Fuso Ecanter is this manufacturer’s light truck. It has a range of 100 km and an MMA of 6 tons. Mitsubishi has put 500 units into circulation in Europe, the USA and Japan. It is possible to see them circulating in New York with the UPS company.
So, it is possible??
The answer is yes and no at the same time. As I mentioned earlier, there are electric models available and in circulation in some cities. There are 2 main problems with these vehicles:
Firstly, the problem we find in all electric vehicles, autonomy. Right now there are no trucks on the market capable of meeting the needs of transport companies for long journeys, so their use is intended for small deliveries.
Second and most importantly, none of the models are already in line production. Volvo will launch production at the end of 2019 and has only put a few models like the Hamburg one into operation. Mercedes will not do the same until 2021 and the 500 trucks distributed by Fuso are rented with a duration of 2 years. During 2019 Fuso will launch series production. Man will not manufacture this model until the middle of the next decade. Therefore, little by little we will see how these vehicles are appearing in the urban deliveries but there is still much to see them on long distances.
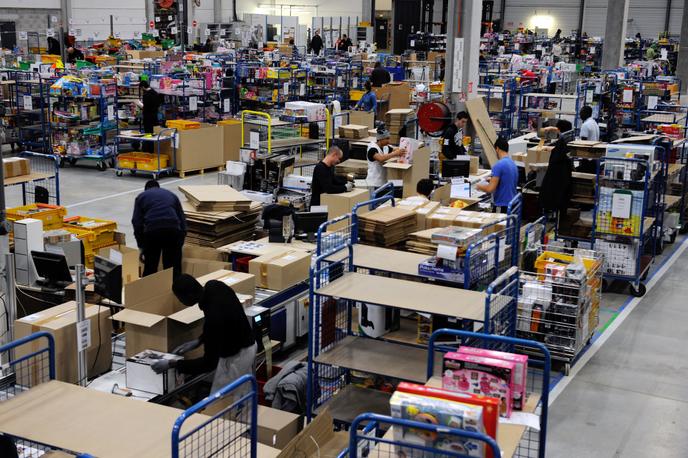
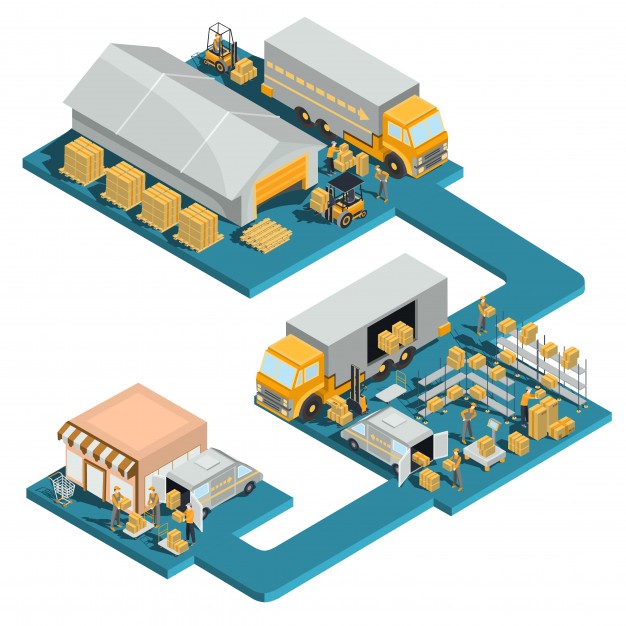




















 The building about a million square feet and employ a thousand associates during the peak holiday seasons. The store millions of units of inventory within the buildings and millions of different types of inventory as well , and ship out tens of thousands of customer orders everyday during peak .
The building about a million square feet and employ a thousand associates during the peak holiday seasons. The store millions of units of inventory within the buildings and millions of different types of inventory as well , and ship out tens of thousands of customer orders everyday during peak .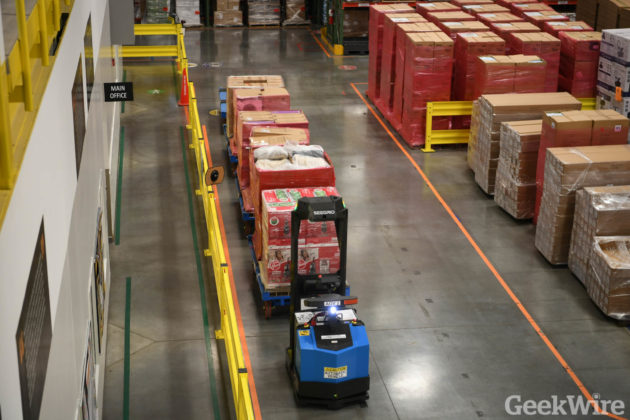
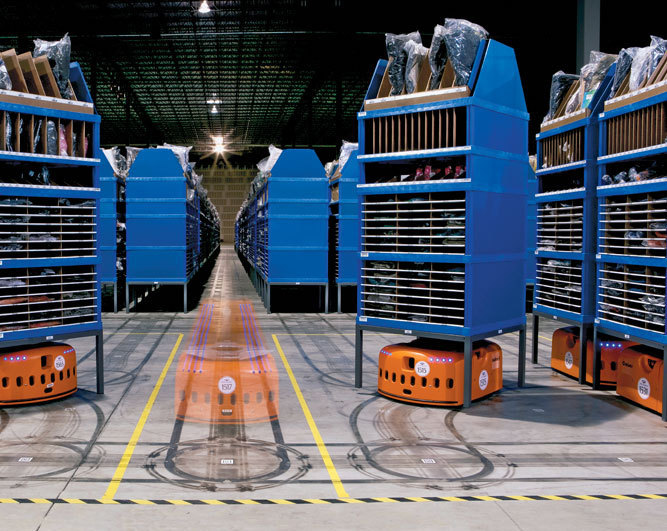
































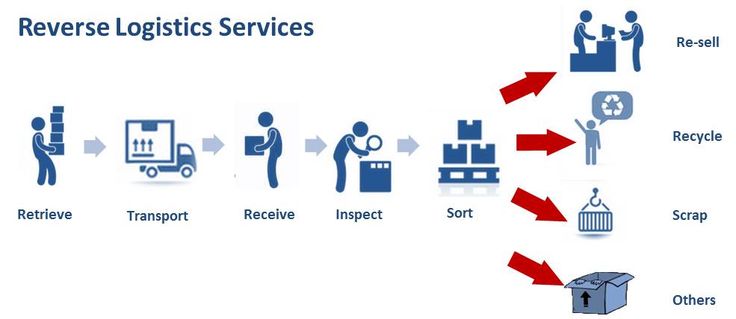
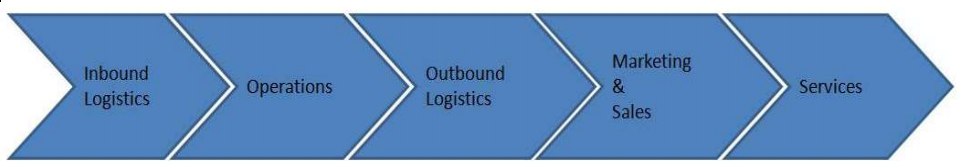


 Overnight shipping is an absolute masterpiece of logistic that happens every single night. It may not be cheap , but you can get a package shipped from Florida on Monday night to Alaska by 8:30 am on Tuesday .The speed and efficiency of these worldwide delivery networks is mind blowing , and it all happens while we sleep .
Overnight shipping is an absolute masterpiece of logistic that happens every single night. It may not be cheap , but you can get a package shipped from Florida on Monday night to Alaska by 8:30 am on Tuesday .The speed and efficiency of these worldwide delivery networks is mind blowing , and it all happens while we sleep .

