The active search for more sustainable transport options is a global trend in a lot of companies and countries, and Brazil is no exception. In a country completely dependent on its road network for transportation of people and cargo, alternative sources to fossil fuels are always on the agenda.
Electric powered vehicles are undoubtedly one of the main candidates to solve this global issue, and, after gaining relevance in the light vehicle market, the modal is becoming more and more popular also in the cargo transport. Here are three cases of companies that are implementing electric vehicles in their operations in Brazil:
- Braspress, Brazil’s leading parcel transport company, increased its electric fleet, buying 30 more electric vehicles from JAC Motors in the first quarter of 2022.
- Ouro Verde, another traditional transport company, also started betting on electric vehicles on its fleet. The company announced an investment of over 18 million euros at the beginning of 2022, 50% of which would be destined to the purchase of electric vehicles.
- The international beverages producer AMBEV, on its turn, has the audacious goal of using only clean energy powered trucks as of 2025. The company announced the purchase of 1000 electric trucks in a partnership with the startup Fábrica Nacional de Mobilidade (FNM). The entire fleet, which is scheduled to be available by the end of this year, will represent a yearly cut of 128 thousand tons of greenhouse gasses – in comparison to trucks powered by fossil fuel.

Electric truck from AMBEV’s fleet.
However, one of the biggest barriers that hinder the popularization of this modal in the logistic operations of Brazilian companies is still the big price difference between electric and fossil fuel powered vehicles, more accentuated than when compared to other regions, such as Europe. In October 2022, prices were varying between 85,000 and 220,000€, for vehicles between 12 and 14 tons, with autonomies varying between 110 and 250 km.
But the increased presence of Hitech Electric in the national market may represent the beginning of the change in this scenario: the Brazilian company, which has already been operating for five years as an importer and developer of electric vehicles, officially announced the launch of the first assembly line exclusively for 100% electric utility vehicles in Brazil, evidencing its transition to an automotive assembler.
The line was implemented in a new factory with a total area of 10,000 m² and started operations in March of this year. It will be dedicated to small utility vehicles that will be equipped with batteries from WEG, a Brazilian company that will supply the Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) set. In addition, all electric vehicles produced by Hitech will be able to receive an additional battery to extend their autonomy.
Rodrigo Contin, CEO of Hitech Electric, stated:
“We now have different electric models for transporting goods, tailor-made to meet last-mile needs for parcels and deliveries, as well as super-applications, urban deliveries, e-commerce networks, among others. Our models generate a drastic reduction in the operational cost of companies. Besides driving the expansion of the industry in Brazil, our models also bring advantages to the environment: zero carbon emission”.
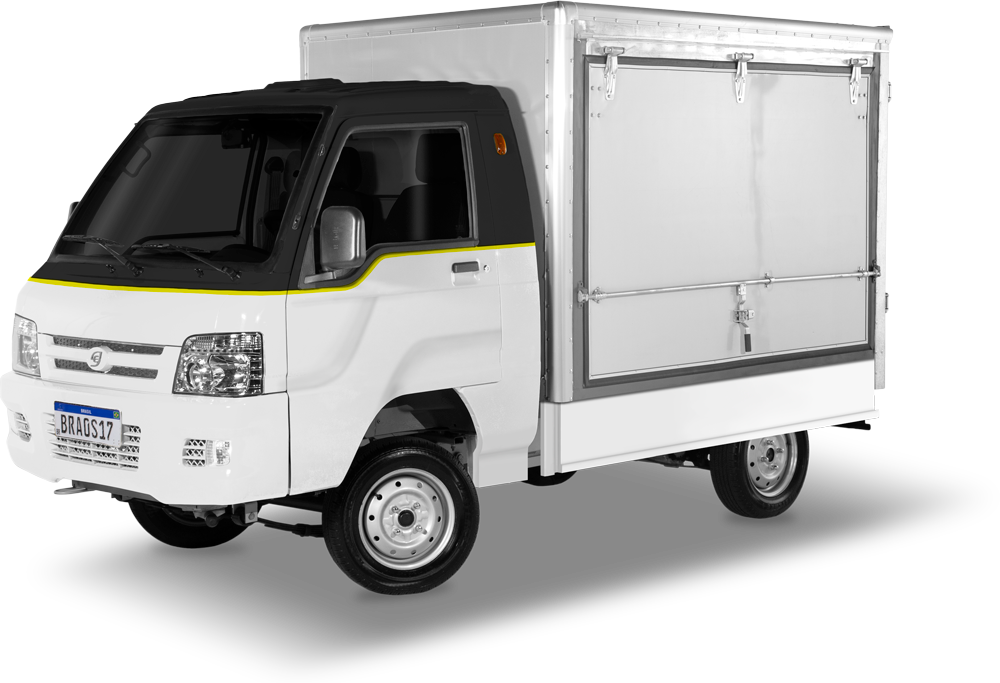
In the first stage, the assembly capacity is 50 vehicles per month, which may expand to 100 units in a short time. The trucks with nationalized assembly are the e.coTruck, with bucket, and the e.coCargo, with trunk. The first costs from 22,500€ and the second has a starting price of 22,800€, both with a load capacity of 800 kg, but the maximum speed is 70 km/h – for comparison, a Kia Bongo with a turbo diesel engine, which is a type of vehicle commonly used in this environment, costs around 28,200€.
e.coCargo: one for the electric models that will be assembled by Hitech in Brazil.
Whether Hitech’s electric trucks will become increasingly popular and competitive in the future, we do not yet know, but according to the company, by now their first batch is already entirely sold. In itself it is interesting to note the emergence of cheaper alternatives for cargo transport based on clean energies, although for countries of continental dimensions such as Brazil, the lack of a rail network for such purposes is unacceptable.